
My Name is Lil Crime
WELCOME TO MY WEB
(Tutorial)
I Build Awesome Experiences from the Ground Up.
WHAT I DO?
I am a I.T Students turned web developer and web designer.
I was always interested in computers, but had no idea you could have a job programming them. As a Designer i taught myself tutorials and CSS, but i really learned how to program at AMA Computer College and different Hacking Groups.
Advice For Aspiring Web Developers
Do not let the "fear of looking like an idiot" get in the way of asking questions or learning new things.Programming is not so different from writing a great paper or learning a foreign language. The biggest barrier to entry is very conceptual. When you approach programming with an intense willingness to learn, amazing things will happen.

BASIC WEB CONCEPTS
LESSON 1: Basic Web Concepts
Web Design
Terminoly
History of
The Internet
History of the
world wide web
Accessing the
Web
Web
Browser
Web Browser
Elements
Kinds of
Web Browsers
Basic Web
Design Principles
Essential Elements
of Web Contents
Planning your
Website
WEB DESIGN TERMINOLOGY
Network - is defined as several computer connected together with purpose of sharing resource including data, information and hardware.
Internet - is a worldwide collection of computers connected to one another sharing wired or wireless including all computers that we use at home, in schools, offices and many other places.
World Wide Web - is a collection of resources and information interconnected via the internet.
Web page - is a formatted page within a website that may contain text, graphics, video and multimedia. This page can be viewed and explored on the internet by the use of program called Web browser.
Splash page - may precede the home page. It usually contains a multimedia which is designed to be attractive and intriguing in order to create curiosity and invite anyone to see its contents.
HISTORY OF THE INTERNET
 The internet has its history anchored on the project started by the United states Government called DARPA (Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency) an agnecy of UD Department of Defense for the development of new technology for military use which was established in 1958. The original name of this agency was simply APRA (Advanced Research Projects Agency) then was renamed to DARPA. The Agency as then headed by J.C.R Licklider in 1962, he installed three computer network terminals, one for the University of California, Berkeley for the Project Genie, one for system Development Corporation in santa, Monica, USA and one at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) for time sharing system projects for advanced computer and networking research. The networking technology led to the development of what we call "Packet Switching", a network communication method that splits the data in chunks, called packets, then reassembled in the correct order at its destination.
The internet has its history anchored on the project started by the United states Government called DARPA (Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency) an agnecy of UD Department of Defense for the development of new technology for military use which was established in 1958. The original name of this agency was simply APRA (Advanced Research Projects Agency) then was renamed to DARPA. The Agency as then headed by J.C.R Licklider in 1962, he installed three computer network terminals, one for the University of California, Berkeley for the Project Genie, one for system Development Corporation in santa, Monica, USA and one at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) for time sharing system projects for advanced computer and networking research. The networking technology led to the development of what we call "Packet Switching", a network communication method that splits the data in chunks, called packets, then reassembled in the correct order at its destination.
 The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) developed the packet switching network standards in 1976 following the research from DARPA called the X.25 CompuServe using the X.25 standard became the first company to offer electronic mail for personal computer users. Several network mnethods ere developed and there was need to unify all of them. Vinton Cerf of Stanford University was recruited by Robert E. Kahn of DARPA to work a solution to this problem. Cerf together with other scientist formulated a common internetwrok protocol, which eventually became the TCP/IP protocol, the only approved standard protocol on the ARPANET.
The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) developed the packet switching network standards in 1976 following the research from DARPA called the X.25 CompuServe using the X.25 standard became the first company to offer electronic mail for personal computer users. Several network mnethods ere developed and there was need to unify all of them. Vinton Cerf of Stanford University was recruited by Robert E. Kahn of DARPA to work a solution to this problem. Cerf together with other scientist formulated a common internetwrok protocol, which eventually became the TCP/IP protocol, the only approved standard protocol on the ARPANET.
Robert E. Kahn, Vinton Cerf, Lawrence Roberts and Leonard Kleinrock recieved the Drapper prize award in 2001 "for the development of the internet". Draper prize is the annual ward given by National Academy of Engineering.
HISTORY OF THE WORLD WIDE WEB
 Sir Tim Berners-Lee is a British computer scientist. He was born in London, and his parents were early computer scientists, working on one of the earliest computers.
Growing up, Sir Tim was interested in trains and had a model railway in his bedroom. He recalls:
“I made some electronic gadgets to control the trains. Then I ended up getting more interested in electronics than trains. Later on, when I was in college I made a computer out of an old television set.”
After graduating from Oxford University, Berners-Lee became a software engineer at CERN, the large particle physics laboratory near Geneva, Switzerland. Scientists come from all over the world to use its accelerators, but Sir Tim noticed that they were having difficulty sharing information.
“In those days, there was different information on different computers, but you had to log on to different computers to get at it. Also, sometimes you had to learn a different program on each computer. Often it was just easier to go and ask people when they were having coffee…”, Tim says.
Tim thought he saw a way to solve this problem – one that he could see could also have much broader applications. Already, millions of computers were being connected together through the fast-developing Internet and Berners-Lee realised they could share information by exploiting an emerging technology called hypertext.
In March 1989, Tim laid out his vision for what would become the Web in a document called “Information Management: A Proposal”. Believe it or not, Tim’s initial proposal was not immediately accepted. In fact, his boss at the time, Mike Sendall, noted the words “Vague but exciting” on the cover. The Web was never an official CERN project, but Mike managed to give Tim time to work on it in September 1990. He began work using a NeXT computer, one of Steve Jobs’ early products.
Sir Tim Berners-Lee is a British computer scientist. He was born in London, and his parents were early computer scientists, working on one of the earliest computers.
Growing up, Sir Tim was interested in trains and had a model railway in his bedroom. He recalls:
“I made some electronic gadgets to control the trains. Then I ended up getting more interested in electronics than trains. Later on, when I was in college I made a computer out of an old television set.”
After graduating from Oxford University, Berners-Lee became a software engineer at CERN, the large particle physics laboratory near Geneva, Switzerland. Scientists come from all over the world to use its accelerators, but Sir Tim noticed that they were having difficulty sharing information.
“In those days, there was different information on different computers, but you had to log on to different computers to get at it. Also, sometimes you had to learn a different program on each computer. Often it was just easier to go and ask people when they were having coffee…”, Tim says.
Tim thought he saw a way to solve this problem – one that he could see could also have much broader applications. Already, millions of computers were being connected together through the fast-developing Internet and Berners-Lee realised they could share information by exploiting an emerging technology called hypertext.
In March 1989, Tim laid out his vision for what would become the Web in a document called “Information Management: A Proposal”. Believe it or not, Tim’s initial proposal was not immediately accepted. In fact, his boss at the time, Mike Sendall, noted the words “Vague but exciting” on the cover. The Web was never an official CERN project, but Mike managed to give Tim time to work on it in September 1990. He began work using a NeXT computer, one of Steve Jobs’ early products.
ACCESSING THE WEB
 The most common means of accessing the internet is through the use of telephone lines. They Existed before computer communications and are widely available worldwide. Although its original intent was for voice Communication, it has now become a vital part of computer communications. Other methods of internet connectivity have introduce to complement the telephone lines. Some examples are; by the use of cables and wireless communications.
The most common means of accessing the internet is through the use of telephone lines. They Existed before computer communications and are widely available worldwide. Although its original intent was for voice Communication, it has now become a vital part of computer communications. Other methods of internet connectivity have introduce to complement the telephone lines. Some examples are; by the use of cables and wireless communications.
Dial-Up Connection - is connecting to the internet using the telephone lines. The method of connection is done like making a cal over the telephone line with the aid of modem (modulator-demodulator).
DSL - or digital subscriber line is also a method of connecting to the internet using the telephone line but provides both data and voice communication, meaning you can use it both to talk and transmit data at the same time unlike the dial-up connection. DSL data trasmission is several times faster and is more reliable compared to the dial-up connection.
Cable Internet - is online connection to the web by the use of cable lines already used by cable television (TV) providers. Cables line can carry TV and data signals faster since they are dedicated line originally intended for TV.
Wireless internet - is internet connection provided by wireless service providers (WSP) wherein wireless enabled computers and gadgets can access to.
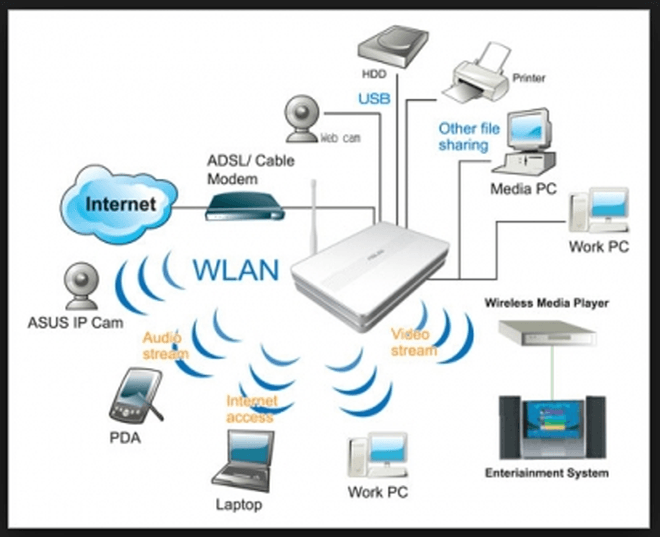
Wireless internet - is the internet using permanent and continuos connection using a "dedicated line" which is of reliable and stable signal for very important internet applications.
WEB BROWSERS
A web site Must be tested and viewed using the broser that are commonly used by users worldwide taht way you will be assured that yuor web site will work in the majority of available brosers out there. This test is important because not all brosers treat some codes the same way. Each broser has its on set of default setting for fonts, background color and so on and the user may also want to modify these setting to thier particular needs or viewing preferences.
WEB BROWSER ELEMENTS
Majority of the web browsers available have the following user interface features in common:
| NAME | FUNCTION |
| Home Button | Usually represented by a house icon to return to the users home page. |
| Address Bar | To input the Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) also known as Uniform Resource Location (URL). |
| Back & Forward Buttons | As represented by left and right arrows, to go back to the previous page and forward to the next. |
| Refresh or Reload Button | To Reload the current page. |
| Stop Button | To cancel loading the current page. |
| Search Bar | As a means to type in topics and terms in a search engine. |
| Status | To display progress of the page being loaded |
| Page Zooming | Capability to view a page closer or further. |
KINDS OF WEB BROWSERS
![]() Internet Explorer (IE) - is a graphical web browser designed and developed by Microsoft Corporation, it is the most popular
internet used by more than 60% of worldwide users.
Internet Explorer (IE) - is a graphical web browser designed and developed by Microsoft Corporation, it is the most popular
internet used by more than 60% of worldwide users.
 Mozilla Firefox - is a free nad open source web browser downloadable from Mozilla.com running on gecko layout engine.Developed by
Mozilla Coporation.
Mozilla Firefox - is a free nad open source web browser downloadable from Mozilla.com running on gecko layout engine.Developed by
Mozilla Coporation.
 Safari - is the web browser for the mac operating system developed and designed by apple Inc using the Webkit (based on KHTML) enegine.Safari 1 was released june 23,2003 and latest version Safari 4 was released june 8,2009.
Safari - is the web browser for the mac operating system developed and designed by apple Inc using the Webkit (based on KHTML) enegine.Safari 1 was released june 23,2003 and latest version Safari 4 was released june 8,2009.
![]() Google Chrome - is a very new web broser from google Inc, the creator of the most popular search engine Google. The Google chrome was released to the public last December 11, 2008 and latest version3 was released September 15,2009.
Google Chrome - is a very new web broser from google Inc, the creator of the most popular search engine Google. The Google chrome was released to the public last December 11, 2008 and latest version3 was released September 15,2009.
 Opera - is the fifth most popular web site as of september 2009 with a share of just 1.5% of the web browser usage. This browser was first released in 1996 and lates version opera 10 was released last june 16,2009 using Presto engine.
Opera - is the fifth most popular web site as of september 2009 with a share of just 1.5% of the web browser usage. This browser was first released in 1996 and lates version opera 10 was released last june 16,2009 using Presto engine.
 Netscape - was the most popular web browser in the 1990s and its firther development has been stopped by its iwner AOL
(America Online) who bought Netscape Communications Corporation.
Netscape - was the most popular web browser in the 1990s and its firther development has been stopped by its iwner AOL
(America Online) who bought Netscape Communications Corporation.
 Flock - is a new web browser that supports Microsoft Windows, Mac OS X and Linux operating system is based on Mozillas Firefox codebase. Flock version 2.5 released on May 19,2009.
Flock - is a new web browser that supports Microsoft Windows, Mac OS X and Linux operating system is based on Mozillas Firefox codebase. Flock version 2.5 released on May 19,2009.
BASIC WEB DESIGN PRINCIPLES
Balance - this concept has something to do with symmetrical andasymmetrical arrangements of the texts and objects of the web page. Symmetrical design suggest traditional , conncervative professional and traditional yet simple mood or atmosphere. Unbalanced or asymmytrical design in common many web sites denotes or conveys energy, modern style and youthfulness.
Proximity - is the replacement of elements with logical relationship close to each other. Proper arrangement of related elements would facilitate user interaction and understanding of the web site.
White Spaces - are literacy blank spaces which are placed around web page elements which allow readability of important text and draw attention to images on the web site.
Contrast - is a way to diffenrentiate the elements of the web page. Contrast is achieve by varying the sizes, character and color of the elements, to arrange them according to which needs to be emphasized and which ones support.
Focus - is the element in the web site which should get the attention of the viewer first.
Unity - is the sense pf agreement and harmony of all the elements of the web site.
Alignment - is the proper arrangement and positioning of the elements of the website.
ESSENTIAL ELEMENTS OF WEB CONTENTS
Accuracy
Readability
Understandable
Concise
Ethical and legal
PLANNING YOUR WEB SITE
Evaluate your Content Copy:
The first thing to do when creating your new website is to evaluate your current copy. If this is your first website, look for materials like existing brochures to establish what content is already available.
Ask yourself three questions.
Is the content correct or still accurate?
Is anything missing?
Is it useful to my readers?
Making sure things are correct will help guarantee you have no outdated pricing or incorrect information.
Determine Your Target Audience:
Before deciding on what content to include on your site, establish who constitutes your website’s target audience. Understanding, or at least identifying, who you are speaking to will help provide clarity as you plan the remainder of your content.
This will also allow you to gauge whether or not information is clear or even necessary. It may help to develop primary, secondary, and even tertiary audiences to make sure that you take into account all of your visitors and their individual needs.
Use Sitemaps as Copy Blueprints:
If you compare creating a website to building a house, your sitemap is like the architect’s blueprint. Without it, you might plan a house that doesn’t have enough bathrooms or closets.
There are many different programs and software suites designed to organize the information. You can use a tool like Microsoft Word’s Organization Chart function or, for more detailed plans, the free cross-platform tool XMind.
Collaborate with Others:
Even if you are the sole person in a business, you will want to include others in the review and editing process to ensure your copy is grammatically correct and that it makes sense to others.
If you work in an organization that requires other stakeholders to weigh in or contribute, there are a variety of methods that can help ease this pain. Try to avoid using one single file for all of your content, as this doesn’t allow for easy collaboration.
Use Storytelling Versus ‘Storyselling’:
You may feel that your website is a chance to “tell your story.” Instead, it should tell the stories of others who have benefitted from using your products or services.
Avoid going on and on about how wonderful your business is. Instead, provide evidence or results. Use language that is familiar to your target audience, not industry-specific terminology.
Appeal to their problems by explaining your product or service as a solution. Provide clear benefits in easy-to-read bullets instead of verbose paragraphs. Making your content user-centered meets users’ needs and tells their story instead of just yours.
Write for Humans and Search Engines:
For those of you who know the importance of writing your copy for SEO, don’t become too focused on injecting your key search terms so many times that the content becomes unreadable. By naturally including your terms throughout the copy on the site, you ensure that once someone gets there, you don’t sound like a robot.
Also, by using “semantic keywords” you can develop a variety of words that provide the same meaning around your core keywords.
If you are a divorce lawyer, for example, don’t say “divorce lawyer” every few words. Instead, use related terms like “family law” or “child custody.” This will help vary your content while allowing you to keep words that support your search efforts.
Make the Copy Action Oriented:
Encourage people to take action once they read your copy. Whether you want them to call you, message you for more information, or buy a product online, tell them what their next step is at the end of your copy. Providing an email address or links to your contact page gives them an easy action to take while your business is still top of mind.
Give the Copy Visual Appeal:
Break up your text up with supporting images, charts, or illustrations. Also, because most people will not read all of your copy but will scan through instead, separate it using larger pull quotes or testimonials, as well as bulleted lists. In addition, keep your paragraphs short and use sub-headings to divide sections.
Choosing the correct typeface plays a significant role in your copy’s legibility. Most web designers recommend using a sans-serif typeface for body copy and a slightly larger serif for headlines. Use of these techniques can help ensure that your copy looks as good as it is useful.
Set Deadlines:
Although it’s easier than ever to edit your own website copy with a content management system like WordPress, this can be the enemy of completing and launching your new website. You will need to set concrete deadlines to make sure your project stays on track. Grouping content creation activities into relevant chunks ensures that you complete tasks on time.
Starting with the about section helps set the tone for your copy and assists in determining what key differentiators to focus on throughout the site. Save the smaller, less copy-heavy pages like contact and locations for the end.
Set initial copy deadlines for your team, schedule reviews by all stakeholders, and, finally, determine when to input all copy into the site.
Planning your website content doesn’t have to be as burdensome as it may seem. By investing time in pre-planning and strategy, the process can be much easier.

HTML TUTORIALS
LESSON 1: Basic HTML
What is HTML?
Writing HTML Files
The Notepad Window
Starting HTML with Notepad
WHAT IS HTML?
The term html is an acronym of Hyper Text Markup Language. It is a markup language used for creating webpages.
WRITING HTML FILES
If you are to write an application letter, a business corresponded or even an excuse letter, you probably used microsoft word or openoofice.org. If you are write html file, you will probably use Notepad. In Writing HTML, you need not high-end software applications because it is easy solely made of pure text. Even a simple text editor can make the job done for you since all that is needed is text file saved in ASCII format.
STARTING HTML WITH NOTEPAD
1. Go to the "Start" button.
2. Click All Programs.
3. Select the Accessories.
4. Select Notepad.
LESSON 2: Tags
What is a Tag?
Structures of Tag
Container & Empty Tags
WHAT IS TAG?
HTML tags are the hidden keywords within a web page that define how the browser must format and display the content.
Most tags must have two parts, an opening and a closing part. For example, is the opening tag and is the closing tag. Note that the closing tag has the same text as the opening tag, but has an additional forward-slash ( / ) character. I tend to interperet this as the "end" or "close" character.
There are some tags that are an exception to this rule, and where a closing tag is not required. The tag for showing images is one example of this.
Each HTML file must have the essential tags for it to be valid, so that web browsers can understand it and display it correctly.
The rest of the HTML file can contain as little or as many tags as you want to display your content.
STRUCTURES OF TAG
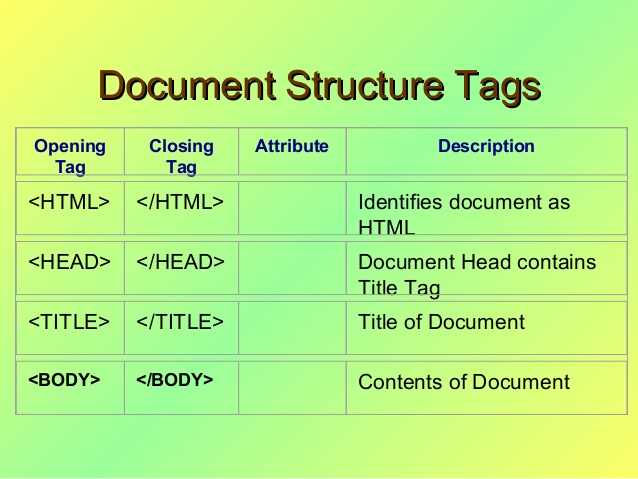
CONTAINER & EMPTY TAGS


JAVA SCRIPT TUTORIALS
LESSON 1: Introduction to Java Script
What is
JavaScript?
What Can
JavaScript Do?
Features of
JavaScripts
Disadvantages of
JavaScripts
How to start Using
JavaScript
Object & its Commonly
Used Properties & Methods

CSS TUTORIALS
LESSON 1: Introduction to CSS
What is CSS?
CSS Structure
Capabilities of CSS
Advantages of using CSS
Three Kinds of CSS
Inline Style
Creating External CSS File
Embed Style
Attribute table for style
Linked Style
.png)
MY PROFILE
Why I Love It?
I get excited about building really fast systems that connect people. Also I fell most inspired when I am thinking through difficult problems with people i admire. That is the best feeling.
Background: IT Support at Philippine Cyber Hacking, Ethical Hacker at Anonywolves PH and DJ at Junji Mix Club.
Proffesional Skills: Anonymous, Network Security, Ethical Haking, Web Developer, Computer Programming, Modder, Creativity.